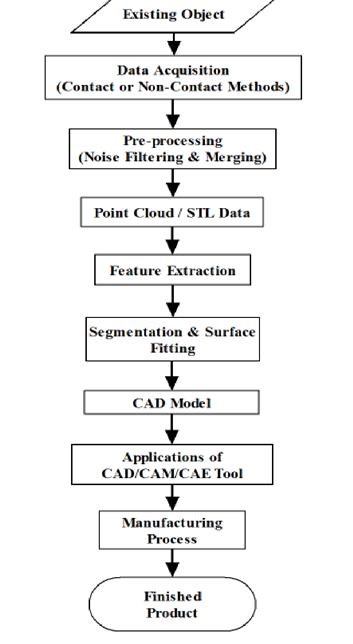
Reverse engineering (RE), also known back engineering is the process of attaining a geometric CAD model from measurements developed by contact or non-contact scanning method of an existing man-made model. In computerized manufacturing the process usually begins by designing a product and finished with machine operation by making a final product from raw materials; CAD file is used in creating and modifying a product design. However, the advantage of reverse engineering is that it compromises geometric models, segmentation, surface fitting and representations to develop accurate CAD models. Engineers prefer reverse engineering above all as it largely reduces the production period and costs in product re-design and research.
Three Digital Convergences Impacting Engineering Sector in the Past Three Decades
Each time when the decade witnessed a technological revolution, the engineering sector was heavily impacted. New technologies surpassed the old ways of completing a task and broke all the barriers between physical and digital forms, thus creating a whole new market and products. 1970 saw signal processing (1D) that brought analogue and digital conversion together as a common language in the telecom industry. Whereas, 1980 ushered in witnessing digitized fonts and pictures via image processing (2D). Paperwork was completely reciprocated with electronic formats which completely changed the way of storing and sharing information.
The recent convergence took place in the 1990s and the early phase saw the incredible blend of the physical and digitized world via geometric processing that is 3D. The amalgamation of reverse and forward engineering has changed the products that were analysed, designed, redesigned, manufactured and marketed.
Creating high-value commercial parts and legacy parts for historical restoration from Scraps
Reverse engineering vis-à-vis product manufacturing and mechanical engineering refers to create engineering designs, models, and documentation data from the existing parts. The technique has shown impressive results in areas like mechanical engineering, animation/entertainment industry, microchips, software engineering, chemicals, electronics, pharmaceutical products etc. As said by The Society of Manufacturing Engineers (SME) “Starting with a finished product or process and working backward in logical fashion to discover the underlying new technology,” we can estimate the significance of reverse engineering in product development.
History
Reverse engineering came into highlight during World War 2 and the Cold War to help the military to replicate enemies’ technology, weapons, and other war equipment. It was the best way to develop spares from the scrapped or broken parts with no further use as they would be frugal. However, today this engineering method has acquired more than that and has encouraged the industrial revolution. It has boomed automotive design, manufacturing, and quality with better non-contact scanning devices, discrete geometry, and computational power. It is comparatively cost-efficient for developing new products, lesser maintenance costs, quality improvements, and doesn’t require prior knowledge of the technology involved in the existing product.
Applications of RE
- Manufacturing Industry
- To launch a 3D virtual model from an existing or scrapped physical part to be used in 3D CAD, CAE, CAM or other suitable software.
- To scrutinize competitors’ products.
- To manage a digital record of own products.
- To measure product functioning and durability.
- To detect potential patent infringement.
- In Aerospace and Ship Hull Craft
- To develop such parts that doesn’t require CAD models.
- To overcome data exchange problems.
- To troubleshoot problems arose from discrepancies between the actual tooling or as-built part and CAD master model.
- Quality assurance via computer-aided examination and engineering analysis.
- Software Industry
- To mine design and implementation format.
- To examine, detect and eradicate system malware and viruses.
- Analysis of an existing system.
- Chemical Engineering
- To determine chemical composition and formula.
- To find better and improved chemical reactions to create better products with higher performance.
- Health Industry
- Replicating, modeling, and imaging of the human’s bone structure.
- To be viewed and physically analyzed before implanting in a human body.
- Reducing risk and cost by saving in theatre time.
- Body parts creation for orthopedic, dental and reconstructive surgery.
- Applying scanned images with element analysis befitting patients.
- To create a wireless hearing aid that is smaller, more sophisticated, and efficient at a lower cost.
If we compare the current year and the year 1970, then we can analyze reverse engineering has come a long way. There was a time when a high-pressure turbine blade was a challenge as there were limited resources to decode highly guarded industry proprietary information. And today, we have technical innovations that have not only changed the reverse engineering process, but also the practice in itself. No doubt, to achieve quality reverse engineered parts, a full invention of engineering design and manufacturing process is required but the whole process is now short and frugal. Companies are dedicatedly practicing RE and digital scanning to obtain more précised geometric information suitable for markets of different niche. It wouldn’t be ambiguous to say that in the coming years we will design products of our choices at our own homes and offices with the help of Reverse engineering and rapid prototyping. The potentials of this technology are only restricted by boundaries of human thinking.
 +91-120-4736400
+91-120-4736400 info@sphinxworldbiz.com
info@sphinxworldbiz.com